Mach 2 Mph - The Mach number (M or Ma) (/m ɑːk/ ; Czech: [max]) is a dimensionless quantity in fluid dynamics that represents the ratio of the flow velocity across a boundary to the velocity. local speed of sound.
U is the local flow velocity with respect to the boundaries (either inside, such as an object submerged in a river, or outside, such as a channel), and
Mach 2 Mph
C is the speed of sound in the medium, in air varies with the square root of the thermodynamic temperature.
Kelly Field: Key In Cold War Speed Race > Joint Base San Antonio > News
By definition, at Mach 1, the local thread speed u is equal to the speed of sound. At Mach 0.65 u is 65% of the speed of sound (subsonic) and at Mach 1.35 u is 35% faster than the speed of sound (supersonic). Pilots of high-altitude aviation vehicles use the flight's Mach number to represent the vehicle's actual airspeed, but the flow field around the vehicle varies in three dimensions, with corresponding variations in local Mach number.
The local speed of sound, and then the Mach number, depends on the temperature of the surrounding gas. The Mach number is mainly used to determine the approximate value to which a flow can be considered incompressible flow. The medium can be a gas or a liquid. The boundary can move through the medium, or it can be stationary while the medium flows through it, or both can move at different speeds: what matters is their relative speed to each other. The boundary can be the boundary of an object immersed in the medium or of a channel such as a nozzle, diffuser, or medium-transmitting wind tunnel. Since Mach number is defined as the ratio of two speeds, it is a dimensionless number. If M < 0.2–0.3 and the flow is nearly steady and isothermal, the compression effect will be small and simplified incompressible flow equations can be used.
Because the Mach number is a dimensionless quantity rather than a unit of measure, it comes after the unit; the second Mach number is Mach 2 instead of Mach 2 (or Mach). This is somewhat reminiscent of the early oceanic sound unit notation (a synonym for understand), which was also the first unit and may have influenced the use of the term Mach. In the decade before the speed of sound in human flight, aeronautical engineers referred to the speed of sound as Mach number, never Mach 1.
The speed of sound (in blue) depends only on the temperature change at altitude (red) and can be calculated from this because density and pressure separately affect the speed of sound. spend each other. The speed of sound increases with altitude in both the stratosphere and thermosphere, due to thermal effects in these regions.
The World's First Supersonic Private Jet Is Being Built
The Mach number is a measure of the compressive properties of a fluid flow: liquids (airs) behave under the influence of compressibility in a similar way at a given Mach number, regardless of other variables.
According to the model in the International Standard Atmosphere, dry air at mean sea level, standard temperature is 15 °C (59 °F), speed of sound is 340.3 meters per second (1.116). ,5 ft/s; 761.23 mph; 661.49 kn) .
Sound speed is not fixed; In gases, it increases proportionally to the square root of the absolute temperature, and since atmospheric temperature generally decreases with increasing altitude between sea level and 11,000 meters (36,089 ft), the speed of sound also decreases. For example, the standard atmospheric model drops the temperature to −56.5 °C (−69.7 °F) at an altitude of 11,000 meters (36,089 ft), with a corresponding speed of sound (Mach 1) of 295 ,0 meters/second (967, 8) ft/s; 659.9 mph; 573.4 kn), 86.7% of the sea level value.
As a measure of the compressibility of a flow, the Mach number can be derived from the appropriate ratio of the continuity equation.
This Is The Only Picture Ever Taken Of Concorde Flying At Mach 2 (1,350 Mph). This Picture Was Taken In April 1985 From A Tornado Fighter Jet, Which Only Rendezvoused For Just
Where L is the characteristic length scale, U is the characteristic velocity scale, p } } is the reference pressure and ρ 0 } is the reference density. The depersonalized form of the continuity equation can be written as:
Where Mach number M = U / c } = U / c } . In the limit where M → 0 }\rightarrow 0} the continuity equation reduces to ∇ ⋅ u = 0 }=0} - this is the standard requirement for incompressible flows.
While the terms subsonic and supersonic, in pure sse, refer to speeds below and above the local speed of sound, respectively, aerodynamicists often use the same terms to refer to certain Mach value ranges. This is due to the emergence of a supersonic regime around the flight (free flow) M = 1 where the approximations of the Navier-Stokes equation used for the subsonic design are no longer valid. apply; the simplest explanation is that the flow around an aircraft wing locally begins to exceed M = 1 ev, even though the free-flow Mach number is lower than this value.
Meanwhile, supersonic mode is often used to talk about the set of Mach numbers for which linearization theory can be used, e.g. the (air) stream is not chemically reactive and can be ignored proper heat transfer between the air and the medium. and calculate.
First Pilot To Exceed Mach 2
In the following table, the mode or range of Mach values is indicated, and not the pure meaning of the words subsonic and supersonic.
In general, NASA defines hypersonic as any Mach number between 10 and 25 and retest speed as greater than Mach 25. Aircraft operating in this mode include the Space Shuttle and space planes. another is under development.
Primarily turboprop and commercial turboprop jets have high aspect ratio (thinner) wings and rounded features such as the nose and leading edges.

The subsonic speed range is the speed range where the total airflow on the aircraft is less than Mach 1. The critical Mach number (Mcrit) is the lowest free-flow Mach number at which the airflow over any set Which part of the aircraft reaches Mach first 1. Thus, the subsonic speed range includes all speeds less than Mcrit.
Approaching Mach 2 In An F 16: 'the Jet Started To Shake'
Supersonic aircraft almost always have swept wings, which cause a delay in towing maneuvers, and are often designed to adhere to the principles of the Whitcomb Area Rule.
The supersonic speed range is the speed range where the airflow over different parts of the aircraft is between subsonic and supersonic. So the flight mode from Mcrit up to Mach 1.3 is called supersonic range.
The supersonic speed range is the speed range where all the airflow on the aircraft is supersonic (greater than Mach 1). But the airflow that meets the leading edges is initially attenuated, so the free flow rate is slightly greater than Mach 1 to ensure that the entire in-plane flow is supersonic. It is generally accepted that the supersonic speed range begins with a free-flow speed greater than Mach 1.3.
Airplanes designed to fly at supersonic speeds show great variation in their aerodynamic designs due to fundamental differences in flow behavior above Mach 1. Sharp edges, wing cross section Thin fans and fully movable tail/nose blades are common. Modern fighters have to compromise to maintain low-speed handling; "real" supersonic designs include the F-104 Starfighter, MiG-31, North American XB-70 Valkyrie, SR-71 Blackbird, and BAC/Aérospatiale Concorde.
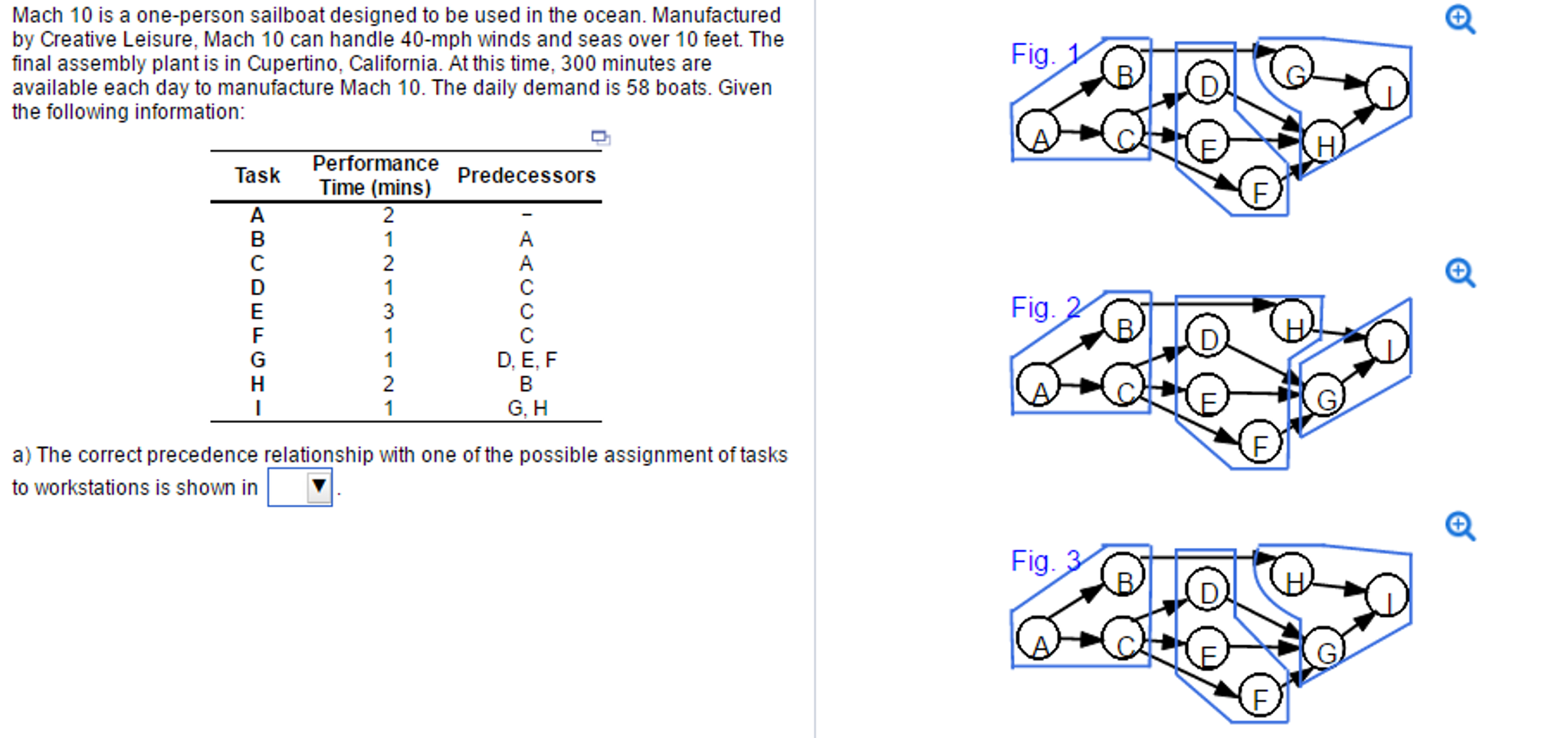
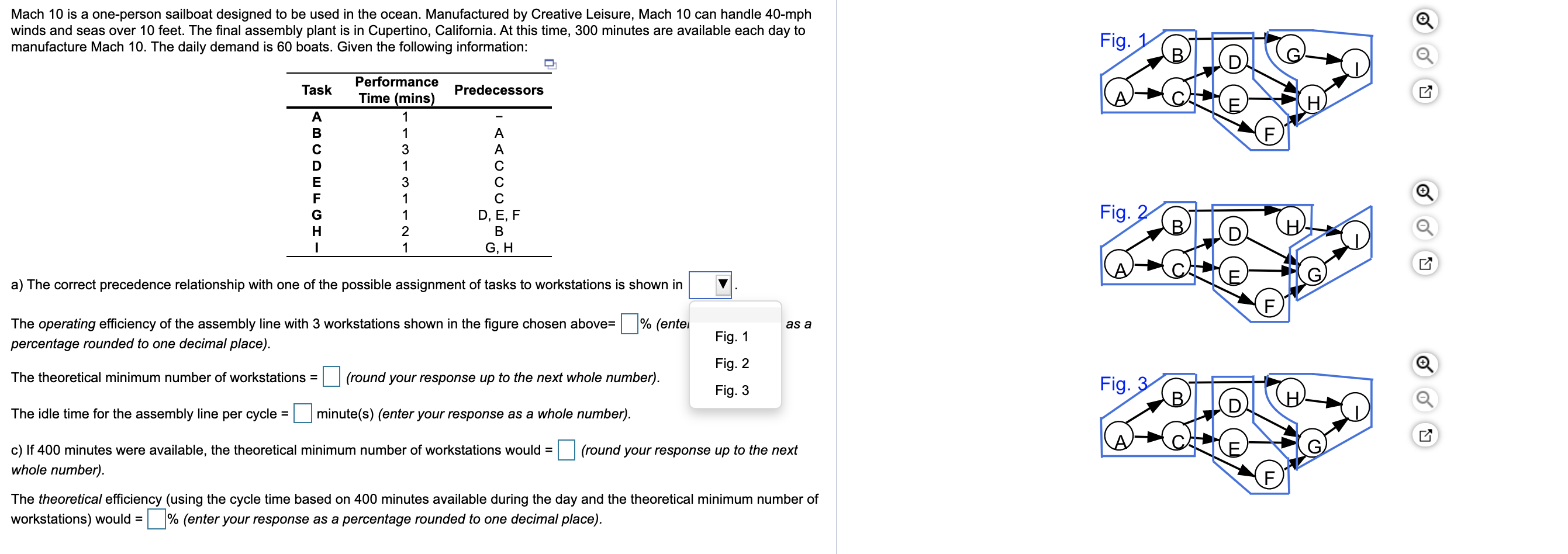
Solved Mach 10 Is A? One Person Sailboat Designed To Be Used
The X-15, with a speed of Mach 6.72 is one of the fastest manned aircraft. The nickel-titanium leather is also cooled; highly integrated (due to the effect of noise: non-linear behavior means superposition of results for discrete components is invalid), small wings, like on Mach 5 X-51A Waverider .
The NASA X-43, with a speed of Mach 9.6 is one of the fastest aircraft. Thermal control becomes a dominant design consideration. The structure shall be designed for hot operation or protected with special silicate bricks or the like. Chemical reaction fluxes can also corrode media shells, with free atomic oxygen at very high rates. Supersonic designs are often forced to have a blunt profile because the aerodynamic heating increases as the radius of curvature decreases.
Ablative heat shield; small or wingless; blunt form. Russia's Avangard (supersonic glider) reaches a speed of Mach 27.

For comparison: the speed required for low Earth orbit is about 7.5 km/s = Mach 25.4 in high-altitude air.
Top 6 Fastest Military Aircraft In The World
At supersonic speeds, the flow field around the object contains both subsonic and supersonic parts. The ultrasonic cycle begins when the first region of the flux M > 1 appears around the object. In the case of aircraft (such as wings), this usually happens on the wings. The supersonic current can only decelerate back to subsonic in a normal shock; This usually happens front and back. (Figure 1a)
As velocity increases, the region of M>1 flows increases towards both leading and trailing edges. When M = 1 is reached and passed, the normal shock reaches the posterior edge and becomes a weak oblique shock: the flow decelerates through the shock, but remains supersonic. A normal shock is generated at the front of the object, and the only subsonic region in the flow field is a small region around the anterior edge of the object. (Figure 1b)
Figs. 1. Mach number in supersonic airflow around the wing; M < 1 (a) and M > 1 (b).
When the aircraft exceeds Mach 1 (i.e. the sound barrier), the large pressure difference occurs only at
B 58 Hustler Mug
Sig p365 tulster holster, sig p365 iwb holster, sig holsters p365, sig p365 sas holster, sig p365 xl holster, sig p365 hybrid holster, appendix holster sig p365, safariland holster sig p365, sig p365 belt holster, sig p365 holster, sig p365 purse holster, sig sauer p365 holster

0 Comments